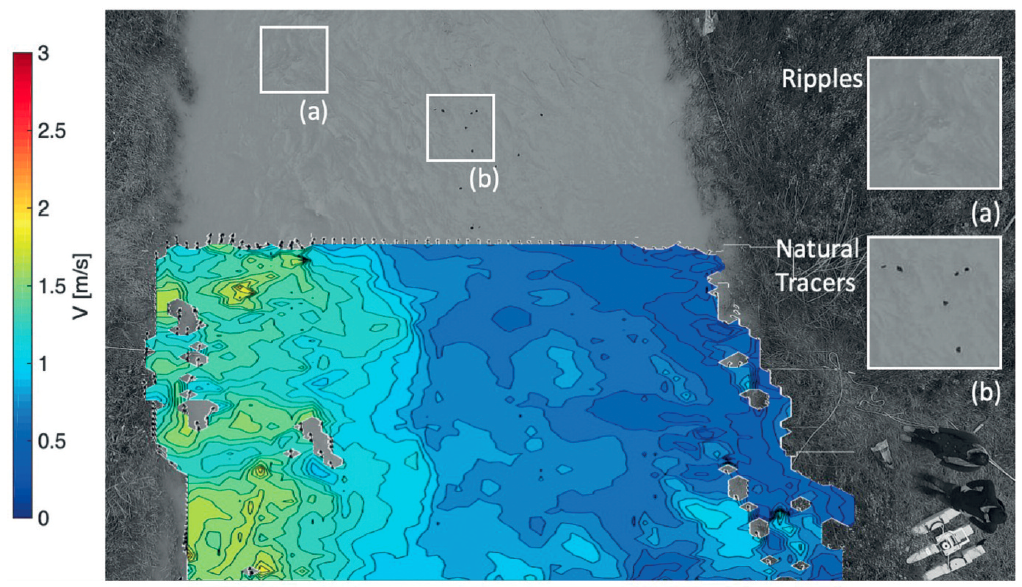
Advances in flow monitoring are crucial to increase our knowledge on basin hydrology and to understand the interactions between flow dynamics and infrastructures. In this context, image processing offers great potential for hydraulic monitoring, allowing acquisition of a wide range of measurements with high spatial resolution at relatively low costs. In particular, the particle tracking velocimetry (PTV) algorithm can be used to describe the dynamics of surface flow velocity in both space and time using fixed cameras or unmanned aerial systems (UASs). In this study, analyses allowed exploration of the optimal particle seeding density and frame rate in different configurations. Numerical results provided useful indications for two field experiments that have been carried out with a low-cost quadrocopter equipped with an optical camera to record RGB videos of floating tracers manually distributed over the water surface. Field measurements have been carried out using different natural tracers under diverse hydraulic and morphological conditions; PTV’s processed velocities have been subsequently benchmarked with current meter measurements. The numerical results allowed rapid identification of the experimental configuration (e.g., required particle seeding density, image resolution, particle size, and frame frequency) producing flow velocity fields with high resolution in time and space with good agreement with the benchmark velocity values measured with conventional instruments.
How to cite: Dal Sasso, S. F., A. Pizarro, C. Samela, L. Mita, and S. Manfreda, Exploring the optimal experimental setup for surface flow velocity measurements using PTV, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190:460, (doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-6848-3) 2018. [pdf]