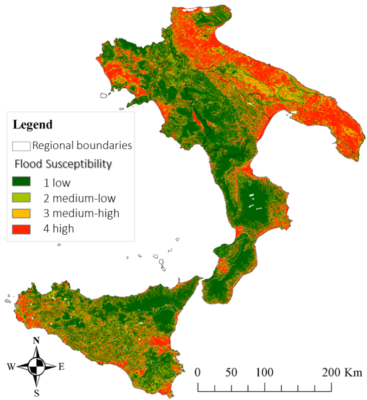
This study suggests a rapid methodology to delineate areas prone to flood using machine learning techniques. Based on available historically flooded areas, the model employs and combines globally collectible and reproducible conditioning factors to analyze flood susceptibility. The flood inventory map includes historically flooded areas from 1920 that occurred over the study area—Southern Italy. The impact of each factor is examined using correlation attribute evaluation and information gain ratio, while the performances of the model are evaluated by using area under receiving operating characteristics. Findings demonstrate that machine learning models can help in quick flood-prone areas analysis, especially in areas where flood hazard maps are not available.
How to cite: Balestra, F.; Del Vecchio, M.; Pirone, D.; Pedone, M.A.; Spina, D.; Manfreda, S.; Menduni, G.; Bignami, D.F. Flood Susceptibility Mapping Using a Deep Neural Network Model: The Case Study of Southern Italy. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021036
